What is Six sigma: Everything you need to know about it
Six Sigma is a data-driven, disciplined methodology and approach for improving processes in organizations. It aims to reduce defects, errors, and variability in processes, ultimately leading to improved quality, increased efficiency, and greater customer satisfaction. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s and popularized by General Electric (GE), Six Sigma has become a widely adopted quality management framework in various industries.
The term "Six Sigma" refers to a statistical measure of process performance. In a Six Sigma process, defects occur at a rate of fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). The goal is to bring processes as close to this level of perfection as possible.
Key principles and components of Six Sigma include:
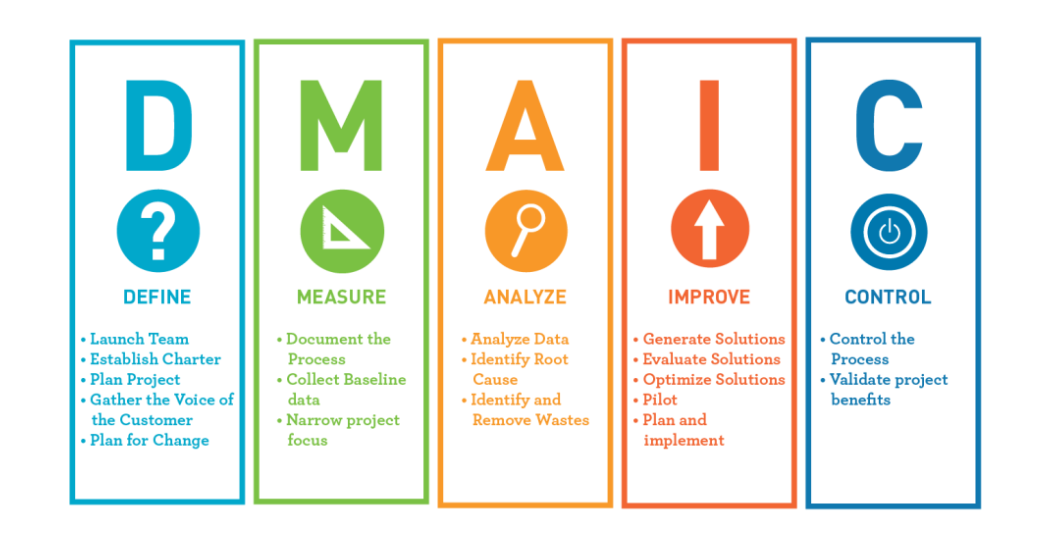
Define: In this phase, the project's goals, scope, and objectives are clearly defined. It involves identifying the problem, determining the stakeholders, and establishing the project's boundaries.
Measure: This phase involves gathering data and measuring the current performance of the process. Metrics are used to quantify the process's baseline performance and identify areas for improvement.
Analyze: During this phase, data analysis techniques, statistical tools, and root cause analysis are employed to identify the factors contributing to defects or process variability. It helps pinpoint the specific issues that need to be addressed.
Improve: Once the root causes are identified, improvements are designed and implemented to eliminate defects and enhance process efficiency. Strategies may include process redesign, automation, or other changes.
Control: In the final phase, control measures and tools are put in place to sustain the improvements achieved. Statistical process control (SPC) charts and ongoing monitoring ensure that the process remains stable and within the desired performance range.
Drive Quality and Efficiency with Six Sigma-Yellow Belt Certification Course at Optiontrain.com
Six Sigma also categorizes individuals involved in the process improvement efforts into different roles, including:
Master Black Belt: Typically a senior leader responsible for promoting and supporting Six Sigma initiatives across the organization.
Black Belt: A highly trained individual who leads complex improvement projects and is skilled in statistical analysis and problem-solving.
Green Belt: A team member who works on Six Sigma projects part-time while maintaining their regular job responsibilities.
Yellow Belt: Has basic knowledge of Six Sigma principles and participates in improvement projects as needed.
White Belt: Has a basic understanding of Six Sigma concepts but is not directly involved in project work.
Benefits of Six Sigma:
Improved Quality: Reduced defects and errors lead to higher-quality products and services.
Cost Reduction: Fewer defects mean lower rework and operational costs.
Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined processes result in quicker cycle times and resource optimization.
Customer Satisfaction: Meeting or exceeding customer expectations leads to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that implement Six Sigma effectively often gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Cultural Transformation: Successful Six Sigma adoption can lead to a culture of excellence, accountability, and a commitment to continuous improvement throughout the organization.
Excellence is not a destination; it's a journey, and Six Sigma is your roadmap.
Challenges of Six Sigma:
Resource Intensive: Implementing Six Sigma can require significant time, effort, and resources.
Resistance to Change: Employees and stakeholders may resist changes to established processes.
Complexity: The statistical and data analysis aspects of Six Sigma can be challenging for some team members.
Overemphasis on Metrics: In some cases, organizations may focus too heavily on metrics and lose sight of the broader goals and customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach to process improvement that has been successfully applied in numerous industries to enhance quality, reduce costs, and drive efficiency. It fosters a culture of continuous improvement and places customers at the center of all improvement efforts. While it has challenges, when implemented effectively, Six Sigma can lead to significant benefits and a competitive advantage for organizations.
Chart Your Course to Quality Improvement with Six Sigma-Green Belt Certification Course at OptionTrain.com
Suggested blogs
Recent blogs


15 April 2025
|